Fracture Repair
Jaw fractures in animals can occur due to various types of trauma, accidents, and underlying dental diseases. These fractures can lead to severe pain, difficulty eating, and potential complications if left untreated and are considered a medical emergency. Fortunately, Missoula Veterinary Dentistry offers comprehensive treatment options to address jaw fractures in our beloved dogs and cats.
Causes and Types of Jaw Fractures in Animals
Jaw fractures in animals can result from traumatic events like falls, car accidents, or fights with other animals. Additionally, certain dental diseases, such as advanced periodontal disease or oral tumors, can weaken the jawbone and make it more susceptible to fractures. Depending on the nature and location of the fracture, jaw fractures in animals can be categorized as:
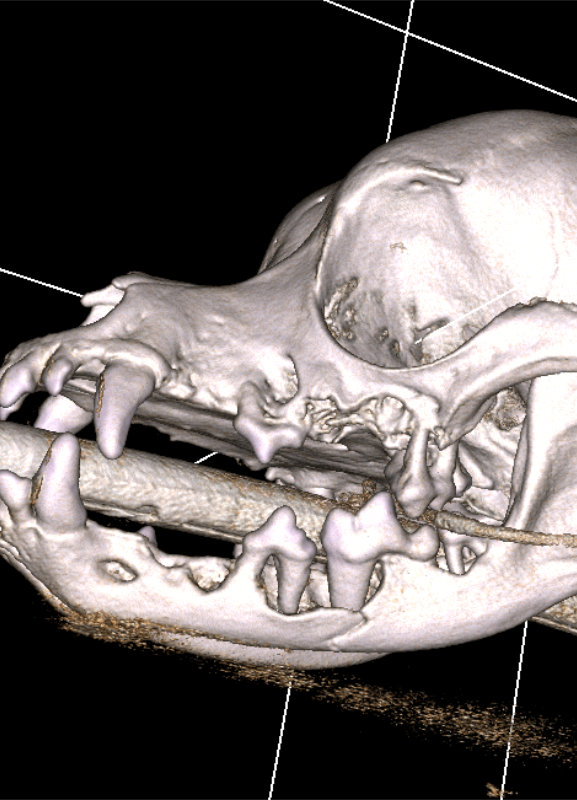
Maxillary Fractures: These fractures involve the upper jawbone (maxilla) and may occur in different regions, including the frontal, zygomatic, or palatal bones.
Mandibular Fractures: Mandibular fractures affect the lower jawbone (mandible) and can occur at various sites, such as the symphysis (midline), body, or condylar region.
The Importance of Prompt Diagnosis
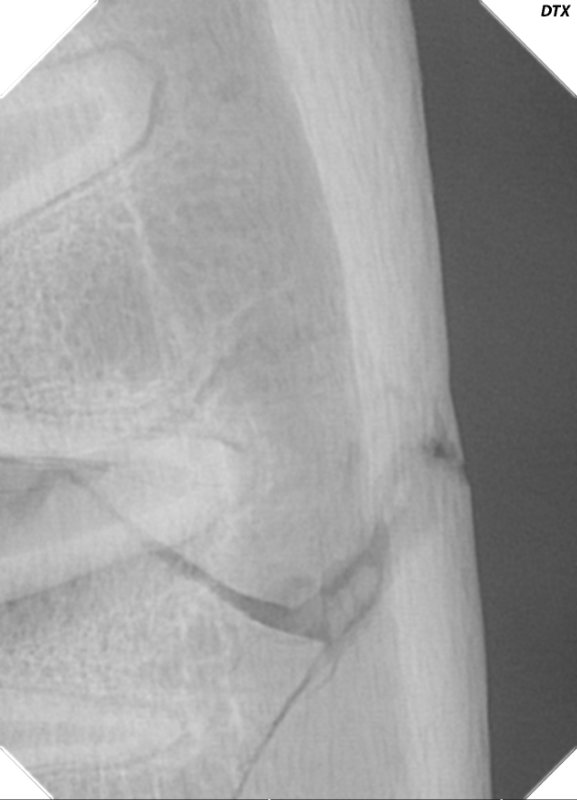
Early diagnosis of jaw fractures in animals is crucial for ensuring appropriate treatment and minimizing potential complications. Veterinary dentists employ various diagnostic techniques, including physical examinations, dental X-rays, and advanced imaging such as computed tomography (CT), to accurately assess the extent and location of the fracture. Prompt diagnosis allows our board certified veterinary dentistry™ team to develop a tailored treatment plan and provide immediate pain relief for each patient.
Treatment Approaches for Jaw Fractures
Conservative Management
In some cases, conservative management may be suitable for less severe fractures, where the bones remain relatively aligned. The animal may be placed on a temporary liquid or soft diet, and pain medication or anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed. Close monitoring is necessary to ensure proper healing and to prevent complications.
Closed Reduction and Stabilization
This technique involves realigning the fractured bone fragments without surgical intervention. Specialized techniques used under general anesthesia are considered minimally invasive and use splints and other temporary appliances to ensure proper alignment of healing bones. Close postoperative monitoring is necessary to assess healing progress and ensure that the animal can eat comfortably.
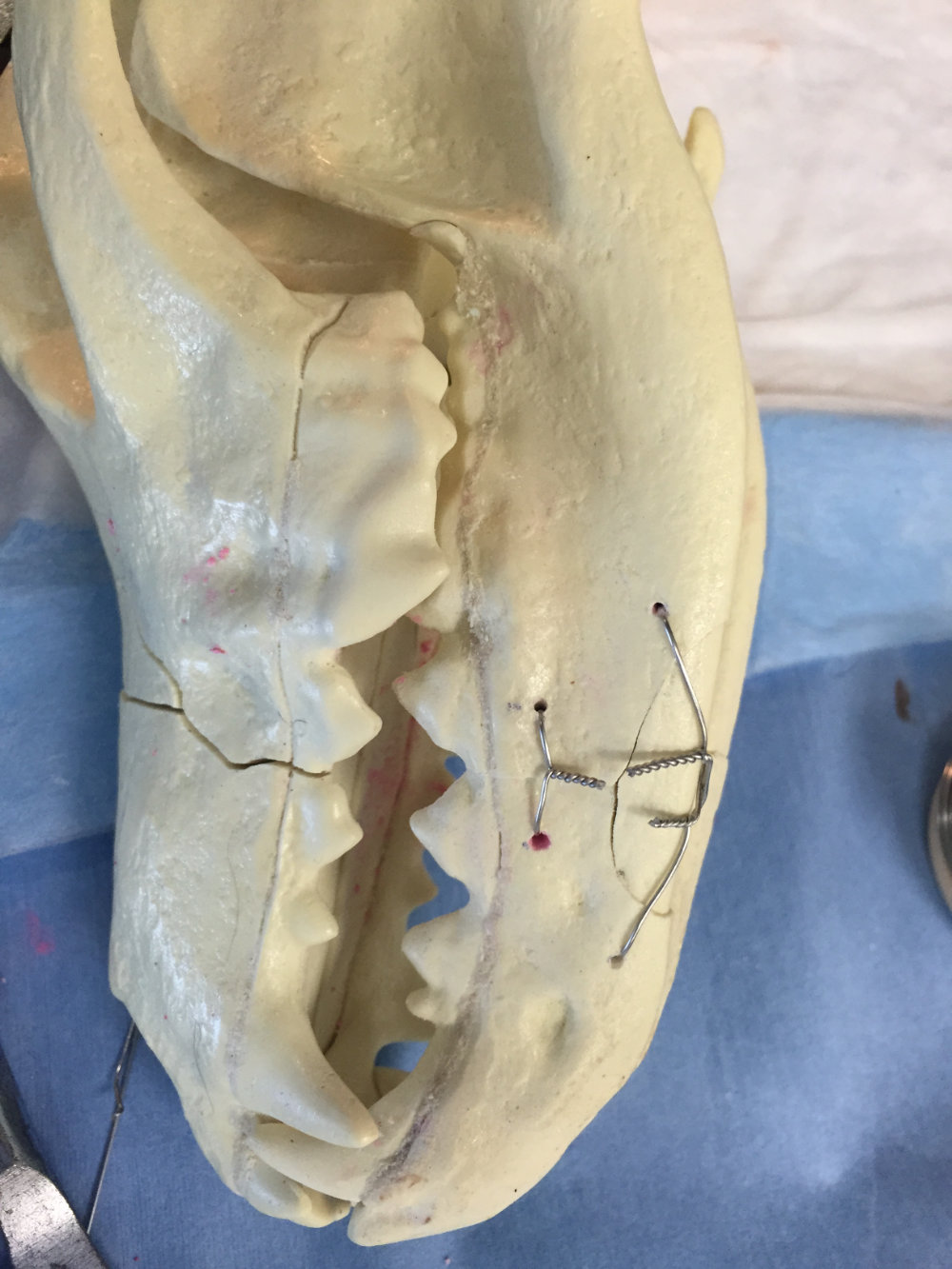
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)
ORIF is a surgical procedure where the fractured bone fragments are exposed and realigned. Veterinary dentists use specialized instruments and techniques to stabilize the fracture site using bone plates, screws, or wires. This approach provides more precise control of the fracture alignment and allows for immediate stability, promoting faster healing.

The Role of Board Certified Veterinary Dentists™ in Treatment
Veterinary dentists play a vital role in the treatment of jaw fractures in animals. They possess the necessary expertise and specialized equipment to diagnose and manage complex dental and oral conditions. Veterinary dentists often work closely with other veterinary specialists, including veterinary anesthesiologists, to develop comprehensive treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific needs.
During treatment, veterinary dentists ensure proper pain management, use precise surgical techniques to realign and stabilize the fractured jawbone, and provide postoperative care and monitoring. They also offer guidance to pet owners regarding postoperative feeding instructions, oral hygiene, and follow-up visits to ensure optimal healing and long-term oral health.